Chaos101
What is Chaos Engineering?
Modern applications are complex, distributed, and dynamic—often built with microservices and deployed on cloud-native infrastructure. With that complexity comes unpredictability. Chaos Engineering is the practice of proactively introducing faults to uncover weaknesses and ensure systems remain reliable under real-world conditions.
Chaos Engineering is the discipline of conducting controlled experiments to build confidence in a system’s ability to withstand turbulent conditions in production.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
In the current state for modern applications, downtime isn't just inconvenient—it can damage reputation, revenue, and customer trust.
Harness Chaos Engineering (Harness CE) helps enterprise teams:
- Minimize risks before incidents occur
- Strengthen service reliability and SLAs
- Validate failover mechanisms and autoscaling
- Enable shift-left resilience testing during delivery
Chaos engineering acts as a resilience gate for production, uncovering systemic gaps in infrastructure, failover, observability, and SRE practices.
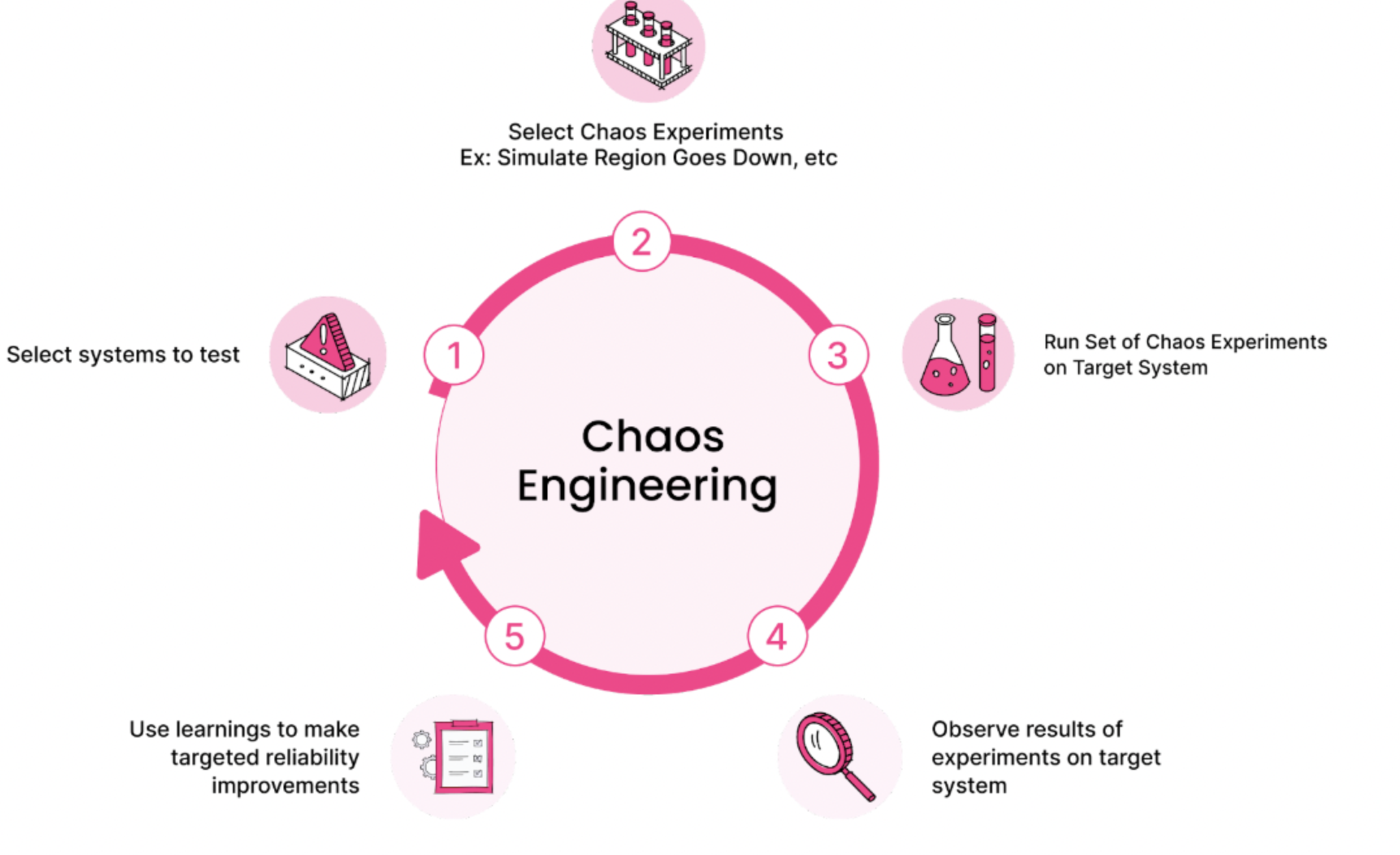
How It Works
Chaos Engineering simulates failures such as:
- Pod or node crashes
- CPU/memory/network stress
- Service/API latency or blackhole
- Cloud infrastructure degradation (for example, EC2 termination, Azure disk loss)
Harness enables this through a structured workflow:
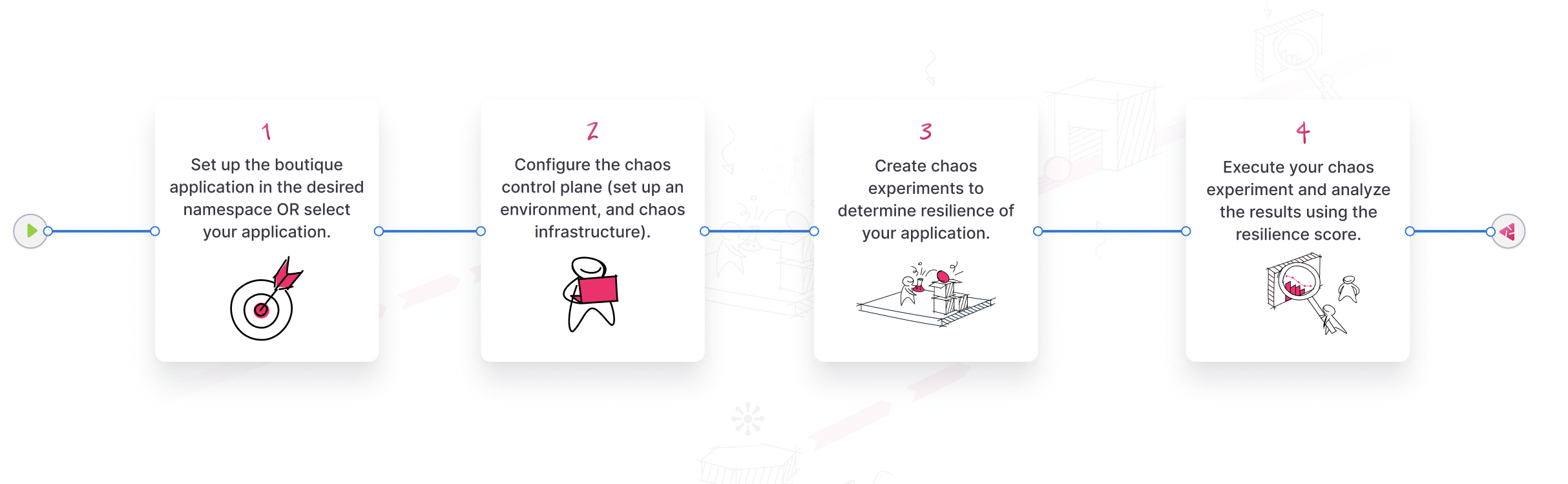
- Define steady state: What does healthy behavior look like?
- Form a hypothesis: What should happen during failure?
- Inject chaos: Simulate the fault with scoped blast radius.
- Observe and verify: Measure if the system maintained its SLOs.
- Remediate and improve: Use insights to harden services.
Built for the Enterprise
Harness Chaos Engineering (Harness CE) goes beyond basic fault injection. It is purpose-built for scale and governance:
-
Governance and Security
- Role-based access control (RBAC) and fine-grained permissions
- Dedicated Workspaces and Chaos Teams for multi-tenancy
- ChaosGuard: Prevent unsafe experiments from executing based on pre-defined conditions
-
Observability and Analysis
- Integrates with APM tools (for example, Prometheus, Datadog, New Relic)
- Health probes, hypothesis validation, and experiment scoring
- Track resilience metrics and experiment impact over time
-
Integrated with CI/CD
- Native integration with Harness CD Pipelines
- Automate resilience testing as part of every deployment
- Enforce resilience gates before production
-
Flexible Experimentation
- Supports Kubernetes, AWS, Azure, GCP, and many more platform-specific chaos injection
- Declarative experiment definition and Git-based chaos artifact sources (chaos-experiments-as-code)
- Rich fault library with reusable and composable chaos scenarios
-
Scalable Architecture
- Built on CNCF LitmusChaos with enhanced enterprise capabilities
- Centralized control plane for managing all chaos infrastructure
- Multi-cluster, multi-cloud support out of the box
Shift Left with Confidence
The initial principles of chaos engineering recommend performing experiments in production, which is relevant and encouraged. This validates resilience beforehand, acting as a quality gate for larger deployment environments. The need to build confidence in a highly dynamic environment—where application services and infrastructure undergo frequent and independent upgrades—accelerates this process. The resulting paradigm includes:
- Increased ad-hoc and exploratory chaos testing by application developers and QA teams;
- Automating chaos experiments within continuous delivery (CD) pipelines.
With Harness CE, resilience is no longer an afterthought. It becomes a native part of the SDLC—from staging environments to production, across every application team.
Next Steps
Ready to inject some resilience into your systems?
Or explore: